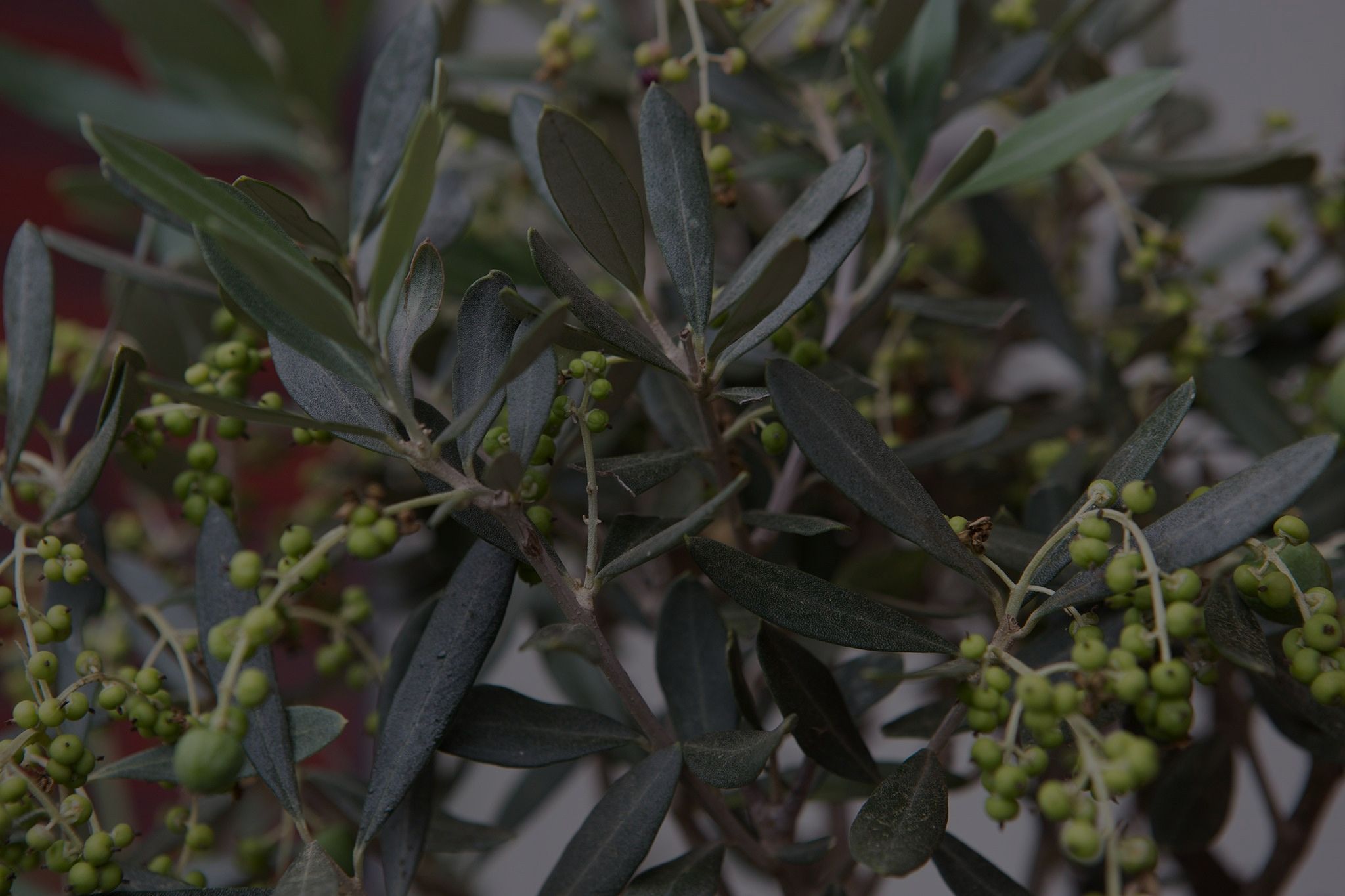
Native to the Mediterranean region, which includes Southeastern Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa, olive trees have long been used to adorn gardens. The scientific name for olive trees is Olea europaea, and they have a long and illustrious history that dates back thousands of years. They are indigenous to the Mediterranean region, which includes sections of the Middle East, Greece, Italy, and Spain.
These unusual trees make lovely garden focus points throughout the year with their silvery foliage, gnarled trunks, and clusters of fragrant white flowers in the spring. Because they yield not only nutritious fruits but also oil for cooking, cosmetics, and religious ceremonies, olive trees have been integral to the cultures and economy of these areas.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about olive tree care and how you can grow these fruiting plants at home. However, you can also opt for various fruitless varieties as well.
Olive Tree Care

Water
Olive trees might be sensitive to overwatering, yet they can withstand drought. Make sure to give enough drainage and let at least half of the soil dry out in between waterings. To allow excess moisture to drain away, potted plants should be propped up on pot feet.
Throughout the growth season, you should water them frequently for healthy flowering and fruit development, particularly if you reside in a hot, dry region. Reduce watering in fall and winter according to the rainfall in your area.
Light
Because they are sun-loving plants, olive trees should be planted in an area that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight each day. Smaller specimens can withstand Eastern light, but they will flourish indoors under an unobstructed South or West window. Olive trees only receive low to moderate indirect light; therefore, don’t put them in windows facing north.
Soil
Use well-draining soil for olive trees. A mix of perlite, pine bark, and compost is recommended for better olive tree care. Even though these plants can grow in a variety of soil types, make sure that the soil you choose isn’t heavy and infertile.
Temperature and Humidity
Native to Mediterranean regions, the olive tree loves hot and dry conditions, but once established, it will also thrive in not-so-severe but cool winters. Keep a temperature range between 50°F and 85°F (10-29°C). Mature plants can tolerate cooler temperatures, but for a limited time.
Olive trees prefer low to moderate humidity and can tolerate dry air.
Fertilizing
These plants aren’t heavy feeders, and excess fertilization in the soil can affect fruit production. However, if your soil lacks the necessary nutrients, use a balanced fertilizer for olive trees. Furthermore, you can also add a layer of mulch at the base of the plant to retain moisture.
Pruning
Pruning is an important part of olive tree care. However, it should be done carefully with these plants. As olive trees fruit on the previous year’s foliage, do not prune them. Remove any dead or diseased wood and thin other branches just enough to let sunlight and air flow through. Young plants should be pruned to a limit to create a strong foundation.
Harvesting
Olive fruits can be harvested while they are still green or after they ripen completely, depending on how you want to use them. Most fruits need to be cured by sun drying, as they can be bitter even after ripening. Similar to apple trees, olive trees bear fruit every other year. So don’t worry if your plant bears no or fewer fruits after producing an abundance of them in the previous year.
Indoor Olive Tree Care
In colder climates, you can grow dwarf varieties of olive trees indoors as they won’t be able to survive outside. However, indoor olive trees might not bear any fruit. Here’s how you can grow and care for olive trees indoors –
- For better indoor olive tree care, place them in a sunny location where they can receive at least 6 hours of sunlight.
- You won’t have to worry about humidity as these plants can thrive in dry indoor air.
- Dwarf varieties usually don’t grow larger than 6 feet; however, you may prune your plant to keep it in shape or even grow olive trees as bonsai.
- Choose a fertile and well-draining soil mix in a large container with drainage holes.
- Feed the plant using a slow-release fertilizer twice a year – spring and mid-summer.
- As container plants have limited root space, they would require more frequent watering.
- Indoor olive trees would require repotting every 2 to 3 years. When the roots of the plant start poking out of the drainage holes, it is time to repot the plant. Use a pot one or two sizes bigger than the current pot, and use fresh potting soil.

Planting Olive Trees
For beginners, it is recommended to start from a nursery-grown Olive tree, and once you bring it home, you can follow these steps to grow it –
- Select the appropriate location: You should plant your olive tree in a spot that gets at least eight hours of direct sunlight every day. Any low spots where water accumulates should not be used for planting.
- Make a hole: Dig a hole that is the same width as the rootball but a little shallower so that the top of the rootball is barely above the soil line.
- Plant the tree: The tree should be carefully taken out of its pot. It is recommended to untangle any circling roots while causing the least amount of disturbance to the root ball. After planting the tree, fill the hole with dirt and give it plenty of water.
- Weed control: Don’t let weeds grow around your olive tree. Aim for a 3-foot weed-free area surrounding the trunk. As a result, the tree will be able to grow without interference from other plants. Mulch should be applied a few inches from the bark.
- Stake if required: If the tree topples, trim down the top growth or secure it loosely to a stake until the tree is more established and the trunk is more robust.
Common Problems With Olive Trees
These plants are relatively hardy, but without the right olive tree care, they can suffer from some problems, such as –
- Pests – Several pests, such as olive fruit flies, scale insects, etc, can harm the health of your olive tree. The olive fruit fly can ruin the entire crop by laying eggs under the skin of olive fruits. Use insecticidal soap to protect the plant from these pests.
- Diseases – Fungal plant diseases such as verticillium wilt can cause dieback. For better olive tree care, check for any signs of infection and take action promptly.
- Leaf Drop and Yellowing – Olive tree leaves can turn yellow and fall due to multiple reasons, such as lack of sunlight, over- and under-watering. Create a strict watering schedule and make sure to fulfill all the needs of your plant for better olive tree care.
- Fruit Drop – Olive tree might drop premature fruit due to a lack of water or nutrients. Ensure sufficient watering and fertilizing for optimal fruit production.
- Toxicity – The leaves and fruit of these plants contain a substance called oleuropein that can be harmful to pets if consumed in large quantities. Since these plants aren’t pet-friendly, keep them away from the reach of pets, especially indoor plants.
Conclusion
Growing olive trees is easy, as these fruiting plants are very hardy and have minimal care needs. You can also grow olives indoors; however, they might not produce any fruit due to a lack of sunlight. However, these fruiting plants will test your patience as they won’t produce any fruits until after 2-3 years of reaching maturity, and this whole process can take up to 18 years. So if you are up for this challenge, add the olive tree to your plant collection.
Raghav is a talented content writer with a passion to create informative and interesting articles. With a degree in English Literature, Raghav possesses an inquisitive mind and a thirst for learning. Raghav is a fact enthusiast who loves to unearth fascinating facts from a wide range of subjects. He firmly believes that learning is a lifelong journey and he is constantly seeking opportunities to increase his knowledge and discover new facts. So make sure to check out Raghav’s work for a wonderful reading.