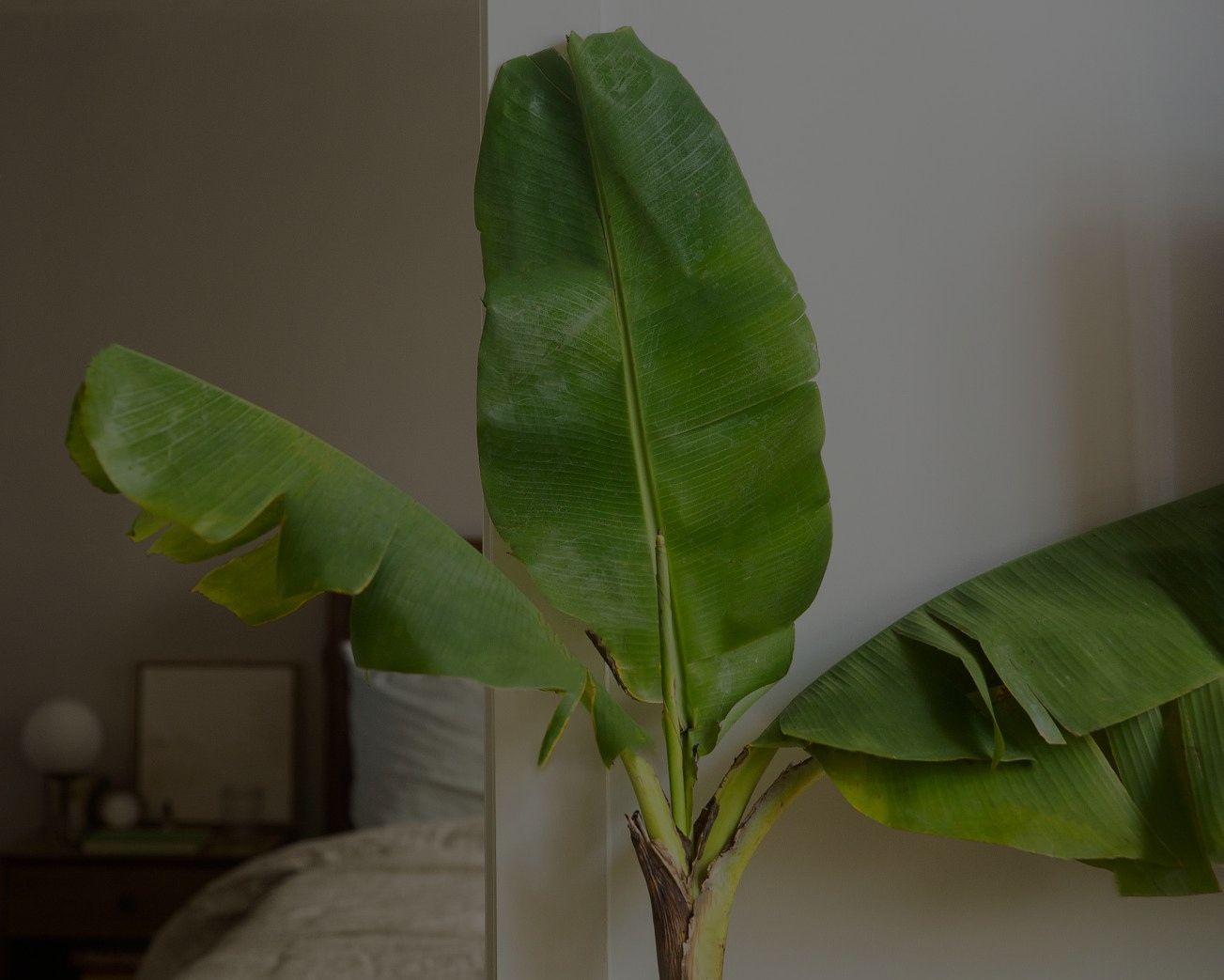
The banana plant is a part of the Musa genus and is a huge herbaceous plant. Originally from Southeast Asia, the banana plant is a tropical herbaceous perennial rather than a tree. There are several types, with variations in fruit size, color, and kind. Some banana plants are prized for their juicy fruit, while others are ornamental. It’s crucial to choose a kind that is appropriate for your area and use.
In many Asian nations, bananas hold great cultural and historical value. They have travelled across countries and been farmed for more than 4,000 years. They have become a mainstay in diets all across the world.
You can easily grow an ornamental or edible banana plant in your home. Banana plant care is easy; however, this plant rarely flowers or fruits indoors. This plant is usually a fast grower and is planted in spring in gardens.
Basic Banana Plant Care

Banana plants come in several shapes and sizes, and their care requirements stay the same –
- Prepare the soil for your banana plant by mixing fresh compost.
- Shelter your banana plant from strong winds, and place it in a location with full sun to partial shade when grown outdoors.
- These plants come in a variety of shapes and sizes; therefore, make sure that you have enough space for your plant.
- Water daily to maintain soil moisture, especially during hot months.
- Applying fertilizers monthly can help during the growing season.
How and When to Plant?
You can grow bananas in gardens or as potted plants indoors. Banana plants should be planted between late spring to early summer when the threat of frost has passed in your area. Choose a location with enough sunlight for optimal growth (6-8 hours).
A place that is shielded from strong winds is preferred for this plant. When planting in containers, make sure to choose a pot that is big enough to support the rootball.
Light
Some banana varieties thrive in full sun, while the leaves of some scorch under direct sunlight and prefer partial shade. For better banana plant care, make sure to provide the right amount of light required by your particular plant.
Provide indoor plants with the maximum amount of sun exposure.
Water
Since this plant is native to tropical regions, it prefers consistent watering and moisture in the soil. For better banana plant care, plant it in groups to retain moisture. Moreover, make sure to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged, as it can cause root rot.
Water the plant early in the morning to ensure adequate water absorption. Additionally, you can use a layer of mulch in the soil to retain moisture.
Soil
Well-draining soil that is high in organic matter is ideal for banana plants. The optimal pH range is 5.5 to 7, which is slightly acidic to neutral. To keep the soil nutrient-rich, add compost or manure on a regular basis. In order to avoid root rot and other issues, proper drainage is essential.
For better banana plant care, think about adding sand to the soil if it is naturally clayey. Berms or raised beds can also help to maintain ideal moisture levels.
Fertilizing
Heavy feeding is required by banana plants. Regular fertilization is beneficial to them, particularly throughout the growing season. A well-balanced fertilizer that is high in nitrogen and potassium can work miracles. A plentiful harvest can be guaranteed by applying the product once a month or by following the manufacturer’s directions.
Additionally helpful are organic fertilizers such as compost tea or worm castings. These enhance soil health in addition to providing nutrition for the plant. Adding trace elements as a supplement will help your banana tree become even more productive.
Temperature and Humidity
They do well in warm, humid environments. They dislike excessive temperatures, so try to maintain a constant temperature between 75°F and 95°F. Frost kills the plants back to the ground, and temperatures below 60°F impede their growth.
Higher humidity is ideal for banana plants. Put a plant (or ordinary) humidifier close by to raise the humidity level.
Pruning
Around the base of banana plants, suckers or puppies frequently appear. These can be propagated, but it’s important to cut off any extra suckers so that only one or two remain. By preventing the division of the plant’s energy, this promotes the growth of better fruit and plants.
Pruning the main stalk back can allow for new growth because once it has fruited, it won’t fruit again. Dead leaves should be removed on a regular basis to maintain the plant looking neat and to keep pests away.
Potting and Repotting
Potting enables you to bring your outdoor banana tree inside for the winter and protect it from cold weather. For best growth, banana plants require at least a 15-gallon container. Use a loose potting mix that is rich in organic matter, and make sure the pot has plenty of drainage holes.
Because they will use the restricted soil more quickly than ground-based banana trees, potted banana trees require more water and fertilizer. Furthermore, they might not produce fruit and probably won’t grow to their full potential. Nevertheless, a lot of people cultivate them for their leaves.
Every three years, container banana trees usually need to be divided and repotted, with any suckers separated from the parent plant.

Common Problems With The Banana Plant
Despite their resilience, banana plants are vulnerable to certain pests such as spider mites and banana weevils. Concerns may also arise from fungal plant diseases. Most of these plant problems may be avoided with better banana plant care, regular inspections, appropriate spacing, and hygienic gardening techniques. Natural pesticides or fungicides are advised if the area is affected.
Marigolds and other companion plants can serve as organic pest deterrents. Potential risks can be further reduced by putting in place a regular cleaning schedule, such as clearing away old or decomposing leaves.
For indoor plants, look out for problems such as root rot, powdery mildew, and leaf spot diseases.
Propagating a Banana Plant
Division is the most effective way to propagate banana trees. Hold off until the suckers have grown their own roots and are at least 12 inches tall.
- Using a sharp garden tool, remove the suckers from the rhizome.
- Give the sliced rhizome a day or so to dry on the surface.
- Replant it at the same depth as the original plant in a pot or in a suitable spot. Keep it moist and water it right away.
Conclusion
Growing a banana plant can be challenging but rewarding. Moreover, banana plant care is easy once you get the hang of it. These fruiting plants can be a staple in your fruit garden, and you can enjoy them at home. By providing the right conditions and care, you can grow this plant easily. So make sure to add this plant to your list and download the Plantora App to learn more about caring for such plants.
Raghav is a talented content writer with a passion to create informative and interesting articles. With a degree in English Literature, Raghav possesses an inquisitive mind and a thirst for learning. Raghav is a fact enthusiast who loves to unearth fascinating facts from a wide range of subjects. He firmly believes that learning is a lifelong journey and he is constantly seeking opportunities to increase his knowledge and discover new facts. So make sure to check out Raghav’s work for a wonderful reading.