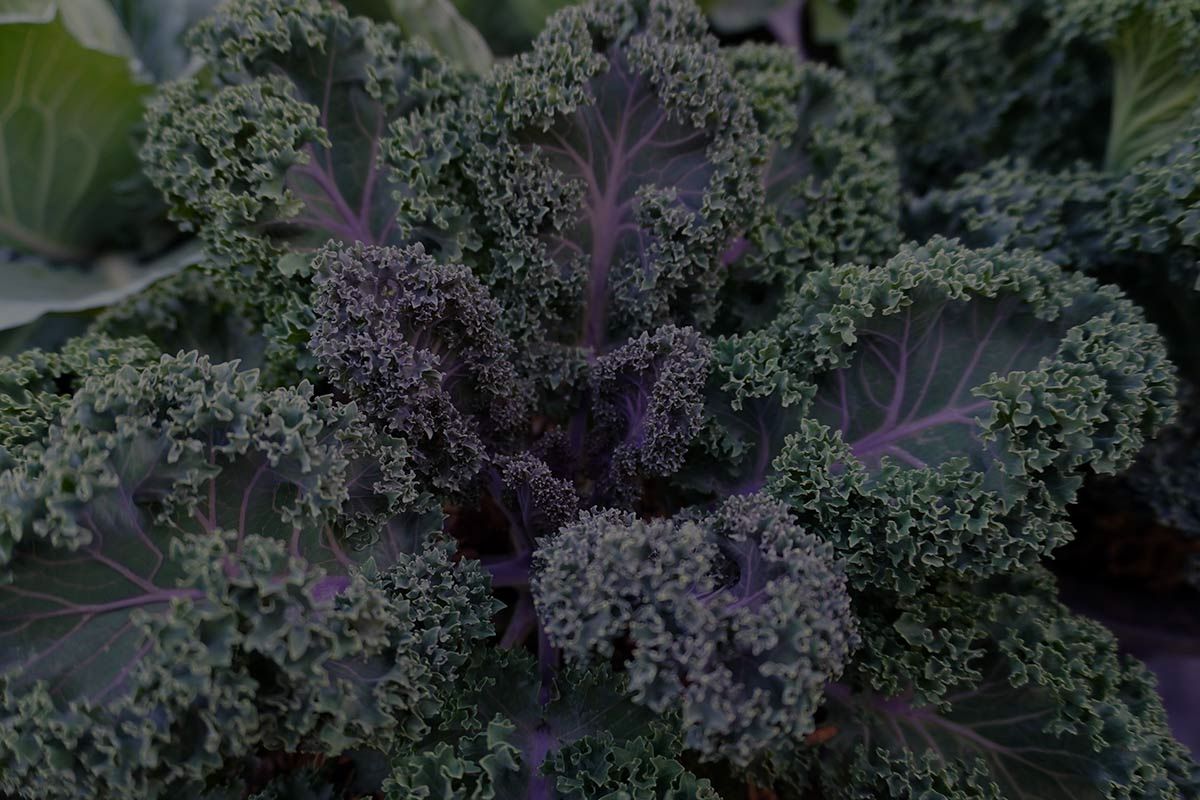
The Kale plant (Brassica oleracea) is a nutritious edible plant that is a part of the cabbage family. This plant has a slightly different appearance from the traditional cabbage. Kale is a winter-loving plant that thrives in chilly temperatures.
This plant comes in various varieties that feature purple, pink, red, and green foliage, so you can use it as a decorative plant in your garden.
The ruffled and textured leaves add aesthetics to the overall appearance of this plant. Kale plant care is easy, and it is a fast-growing plant that can reach the harvesting stage within 3 months. However, it takes two years for this biannual plant to finish its growth cycle; it produces leaves in its first year and seeds and blooms in its second.
This guide will help you get started on growing your own Kale plant and teach you everything about Kale Plant Care.
Kale Plant Care

Water
Kale typically grows best with 1 to 1 1/2 inches of water each week, so it needs a steady supply of water to keep healthy. To keep the soil uniformly moist but not soggy, water your kale plants on a regular basis. In addition to mild weather, wet soil keeps kale leaves crisp and sweet instead of tough and bitter. Mulching the area around your plants can help the soil stay moist and cool.
Light
Since kale grows best when it receives six or more hours of direct sunshine on most days, it requires full sun to moderate shade in most climes. However, give your plant some shade if you live in a hot, dry area, especially from the intense afternoon sun. Heat can make the leaves wilt and lose their flavor.
Soil
Rich soil that is abundant in organic matter and has a slightly acidic pH (6.5 to 6.8) is ideal for kale plant growth. For healthy leaf growth, organic matter’s high nitrogen content is essential. For better kale plant care, choose well-draining soil.
Temperature and Humidity
Once fully grown, the plant can withstand some frost and is typically regarded as a cool-weather food. For better kale plant care, the ideal soil temperature should be between 60 and 65 degrees. All types will benefit from a little frost to make them sweeter and love cool weather. Kale becomes bitter in hot heat.
Although it is typically grown as an annual, kale is a biennial plant that takes two growing seasons (or years) to complete its life cycle. If exposed to severe snowfall or frost, it will collapse.
Fertilizer
Add fertilizer to the top 3 to 4 inches of soil before planting. Then, as directed on the label of the fertilizer, feed your kale during the growing season. For better kale plant care, use a high-nitrogen vegetable fertilizer or compost.
Pruning
Pruning kale is usually not necessary, but if the upper leaves of the plant are infested with pests, you might want to cut it back to the ground. Pruning will not impede the bolting process of kale plants. The bolted leaves are less bitter than other bolted greens, so you can eat them.
When To Plant Kale?
Growing quickly and maturing before summer heat (before temperatures rise beyond 75°F/24°C) or after fall frosts is when kale tastes its best. Even 25°F (-4°C) does not cause significant harm to young plants. Mature plants can tolerate extremely low temperatures since they are exceedingly hardy. Hot weather, however, will impede growth and result in an unpleasant taste.
For spring, you can plant four to six weeks ahead of the typical last spring frost, whether you’re transplanting start plants from the nursery or directly seeding into the ground. Even at soil temperatures as low as 40°F/4°C, seeds will sprout.
Choose early-maturing cultivars for the fall and direct-seed three months before the first date of the fall frost. Note: You’ll need to wait until the weather starts to calm down before planting in regions with hot summers. The sweet, nutty flavor of kale, which can survive strong frosts (25–28°F) without suffering damage, is enhanced by the cool fall weather.
In areas with mild winters, such as the Southwest, Pacific Northwest, and Southeast, kale can also be grown as a winter vegetable outdoors or under cover. All winter long, they will continue to grow and produce. To find out if and when to plant winter veggies, we advise contacting your local cooperative extension.
How To Plant Kale?
The ideal place to plant kale is in full sun since it grows quickly. Space the kale seeds at least 1 1/2 to 2 feet apart and plant them approximately 1/2 inch deep. A few inches of organic matter, such as compost, added to a well-draining soil mixture will promote a good harvest because kale needs a high nitrogen concentration in the soil to grow its leaves.

Harvesting Kale Plant
You should allow around two months for your kale plants to grow from seed. For a more accurate time, look at the days to maturity listed on the label of your plant or seed packet. Kale sown in the spring can be harvested all summer long, but it tastes particularly nice after a little frost.
You can let your plants mature so you can use them as a cooked green, or harvest young kale leaves to use fresh in salads. Let the center of the plant continue to produce after removing the older outer leaves. Kale will keep for around a week in the refrigerator, preferably in the crisper drawer.
How To Propagate The Kale Plant?
You can easily propagate your kale plant using cuttings. Keep in mind to choose the oldest leaf for this process. Here’s how you can propagate Kale –
- Select a stem with several leaves from the main stem and cut it off from the bottom of the plant on its side using gardening shears (do not propagate from the center of the plant). On the lower portion of the stem, remove the leaves. At a 45-degree angle, trim the stem’s base directly beneath a leaf node.
- Apply rooting hormone to the cut end.
- In a tiny container with drainage holes, plant the lower half of the stem in a moistened soilless potting mix.
- Maintain the growth medium’s moisture content. It should take a few weeks for the roots to grow. You’ll know roots have grown if you can lightly pull on the stem and feel resistance. It is then prepared for transplantation.
Common Pests and Disease Problems
Kale belongs to the cabbage family, which is well-known for rot diseases and for drawing pests. Aphids, cabbage loopers, cabbage worms, cutworms, flea beetles, slugs, and black rot and clubroot can all harm kale. For better kale plant care, regularly check them for feeding or egg-related symptoms, including holes in the leaves. Address issues as soon as they appear.
Conclusion
Kale plant care is easy, and you can grow this plant in your garden by following the right steps that are mentioned in this article. This delicious and nutritious plant can be used in various dishes. So make sure to grow this plant with edible leaves and create a vast vegetable garden. Download the Plantora App and learn more about growing such plants easily at home.
Raghav is a talented content writer with a passion to create informative and interesting articles. With a degree in English Literature, Raghav possesses an inquisitive mind and a thirst for learning. Raghav is a fact enthusiast who loves to unearth fascinating facts from a wide range of subjects. He firmly believes that learning is a lifelong journey and he is constantly seeking opportunities to increase his knowledge and discover new facts. So make sure to check out Raghav’s work for a wonderful reading.